Temperature Scales
![]()
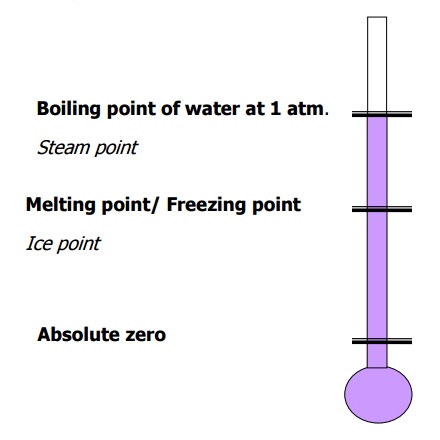
Freezing point of water known as ice point and boiling point of water known as steam point are taken as the reference states for all types of temperature scales.
The various types as temperature scales in use are :
![]()
a) Celsius scale
b) Fahrenheit scale
c) Kelvin scale
d) Rankine scale
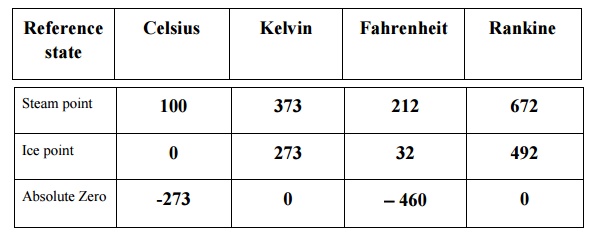
Reference state Celsius Kelvin Fahrenheit Rankine
Steam point 100 373 212 672
Ice point 0 273 32 492
Absolute Zero -273 0 -460 0
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Systems
Matter can exist in any one of the three phases namely solid, liquid and gas. A system consisting of a single phase is known as homogeneous systems. If the matter exists in more than one phase, the system is known as heterogeneous system.
BASIC CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS
Thermodynamics is the science of energy transfer which deals with the relations among heat, work and properties of systems.
The name ‘thermodynamics’ is derived from the Greek words therme, meaning ‘heat’ and dynamis meaning power. Thus, thermodynamics is basically the study of heat and power.
Application Area of Thermodynamics
Energy transfer is present in almost all the engineering activities. Hence, the principles of thermodynamics are playing vital role in designing all the engineering equipments such as internal combustion engines, rockets, jet engines, thermal and nuclear power plants, refrigerators etc.

