Types of Thermodynamic Systems
There are three types of thermodynamic systems :
a) Closed System
b) Open System and
c) Isolated System
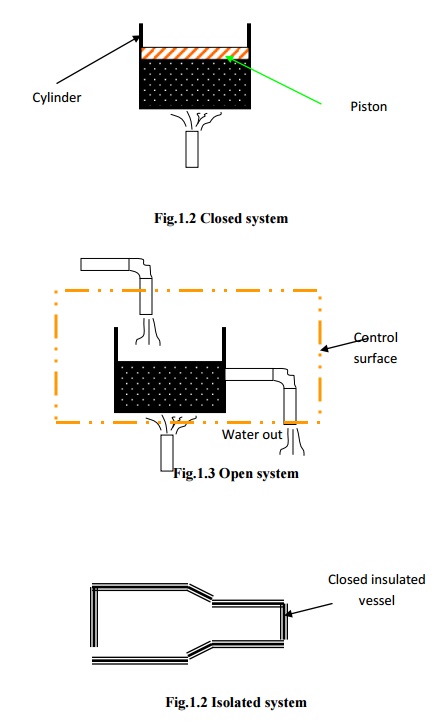
In closed system, attention is focused on a fixed mass. Energy in the form of heat and work (The terms heat and work will be defined in the chapter 2.) can cross the boundary of the system. But there is no mass flow across the boundary. Hence, the possibility of change in volume is always there in the closed systems.
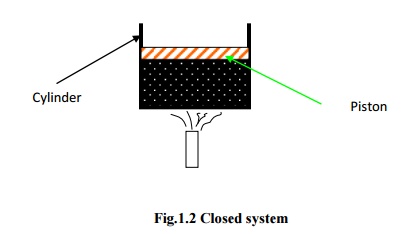
In open system, both matter and energy can cross the boundary. Here, the behaviour of a fixed region in space called control volume is investigated and hence, there is no change in volume. The surface of the control volume is known as control surface.
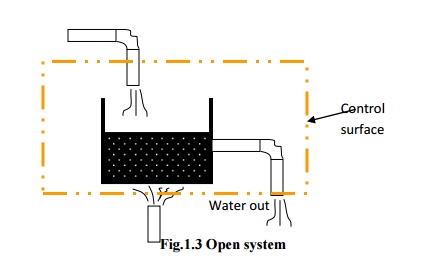
A system that exchanges neither energy nor matter with its surroundings is known as an isolated system.
BASIC CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS
Thermodynamics is the science of energy transfer which deals with the relations among heat, work and properties of systems.
The name ‘thermodynamics’ is derived from the Greek words therme, meaning ‘heat’ and dynamis meaning power. Thus, thermodynamics is basically the study of heat and power.
Application Area of Thermodynamics
Energy transfer is present in almost all the engineering activities. Hence, the principles of thermodynamics are playing vital role in designing all the engineering equipments such as internal combustion engines, rockets, jet engines, thermal and nuclear power plants, refrigerators etc.

