STEPPER MOTOR
1.Phase.
It refers to the no of independent windings on the stator
e.g two phase motors -used in light duty application
three phase phase motor- used in variable reluctance
2. step angle
The angle through which the rotor rotates for one switching change for stator coils
3. holding torque
The maximum torque that can be applied to o powered motor without moving it from rest and causing spindle motion
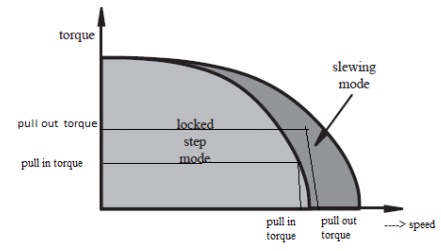
4. pull in torque
The maximum torque against which motor will start or a given pulse rate and reach the synchronism without lose a step
5.pull out torque
The maximum torque that can be applied to a motor running at given stepping rate , without losing synchronism
6.pull in rate
The maximum switching rate at which a loaded motor will remain in synchronism as the switching switching rate is produced
7.slew rate
The range of switching rates between pull in and pull out within which the motor runs in synchronism but cant reverse
characteristics of stepper motor
DC MOTOR .
The major factors in selecting an actuator for mechatronic applications are
• Precision
• Accuracy and resolution
• Power required for actuation
• Cost of the actuation device
The most popular actuators in mechatronic systems are direct current (DC) motors. DC motors are electromechanical devices that provide precise and continuous control of speed over a wide range of operations by varying the voltage applied to the motor.
The DC motor is the earliest form of electric motor. The desirable features of DC motors are their high torque, speed control ability over a wide range, speed-torque characteristics, and usefulness in various types of control applications.

