APPROXIMATE ANALYTICAL METHOD FOR VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION OF THE PISTON
Consider the motion of a crank and connecting rod of a reciprocating steam engine as shown in Fig. 15.7. Let OC be the crank and PC the connecting rod. Let the crank rotates with angular velocity of ω rad/s and the crank turns through an angle θ from the inner dead centre (briefly written as I.D.C). Let x be the displacement of a reciprocating body P from I.D.C. after time t seconds, during which the crank has turned through an angle θ .
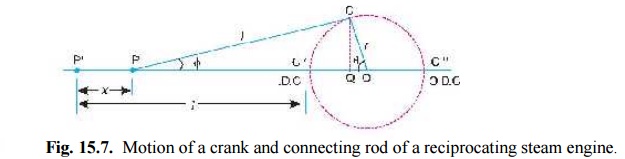
Fig. 15.7. Motion of a crank and connecting rod of a reciprocating steam engine.
Let l = Length of connecting rod between the centres,
r = Radius of crank or crank pin circle,
φ = Inclination of connecting rod to the line of stroke PO, and
n = Ratio of length of connecting rod to the radius of crank = l/r.
Velocity of the piston
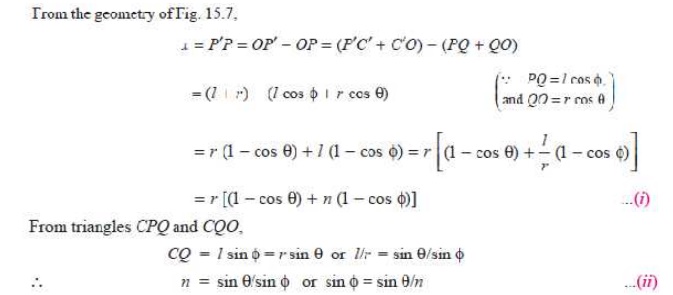
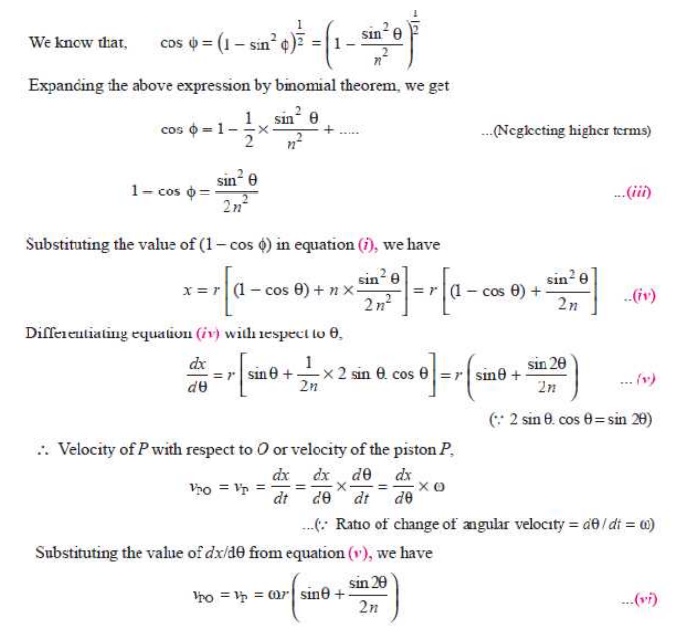
Acceleration of the piston
Since the acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, therefore acceleration of the piston P,
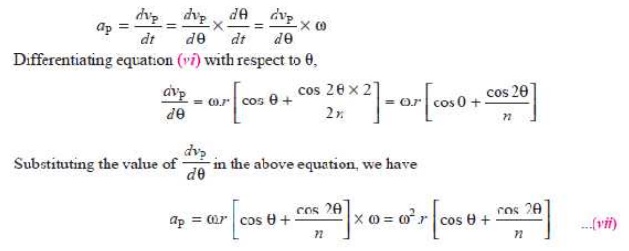
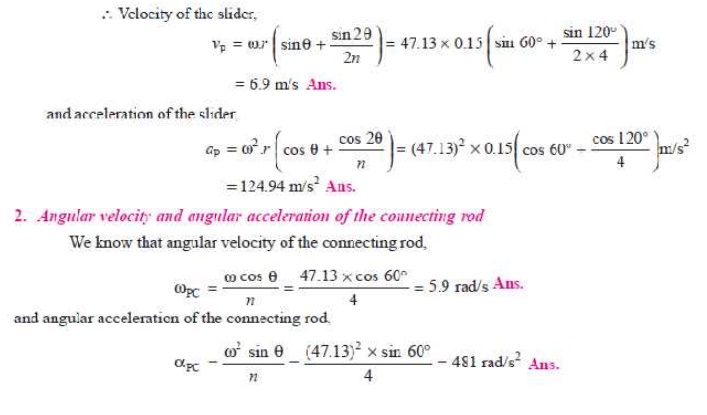
Q.In a slider crank mechanism, the length of the crank and connecting rod are 150 mm and 600 mm respectively. The crank position is 60° from inner dead centre. The crank shaft speed is 450 r.p.m. (clockwise). Using analytical method, determine: 1. Velocity and acceleration of the slider, and 2. Angular velocity and angular acceleration of the connecting rod.
Solution. Given : r = 150 mm = 0.15 m ; l = 600 mm = 0.6 m ; θ = 60°; N = 400 r.p.m or ω = π × 450/60 = 47.13 rad/s
1. Velocity and acceleration of the slider
We know that ratio of the length of connecting rod and crank,
n = l / r = 0.6 / 0.15 = 4