Units of Work and Power
In the international system (SI), the unit of force is Newton (N) and that of distance is metre (m). Hence the unit of work is Nm which is also given a special name Joule. In most of the applications large quantity of work is involved. Therefore kJ is commonly used.
Rate of doing work is known as power. Hence its unit is Nm/S or J/S which is again given a special name Watts(W).
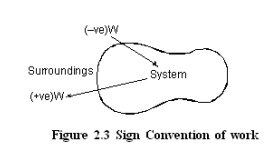
Sign Convention of Work
· Work done by the system on the surroundings is considered as positive work.
Work done on the system by the surroundings is taken as negative work.
Displacement Work
Consider a piston cylinder arrangement as given in the Figure 2.4. If the pressure of the fluid is greater than that of the surroundings, there will be an unbalanced force on the face of the piston. Hence, the piston will move towards right.
BASIC CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS
Thermodynamics is the science of energy transfer which deals with the relations among heat, work and properties of systems.
The name ‘thermodynamics’ is derived from the Greek words therme, meaning ‘heat’ and dynamis meaning power. Thus, thermodynamics is basically the study of heat and power.

